I conducted an in-depth investigation of a newly collected EEG dataset to explore whether measurable differences exist between individuals with high and low hypnotizability. The study focused on two key aspects: spectral power and functional brain connectivity.
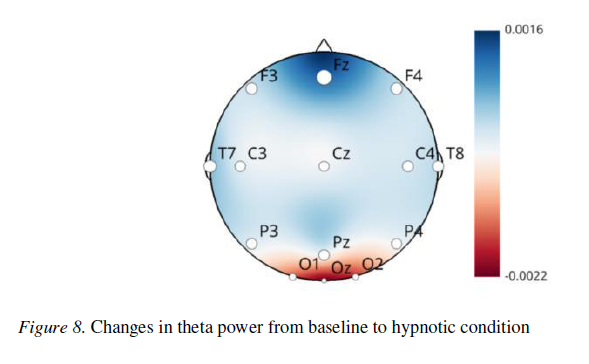
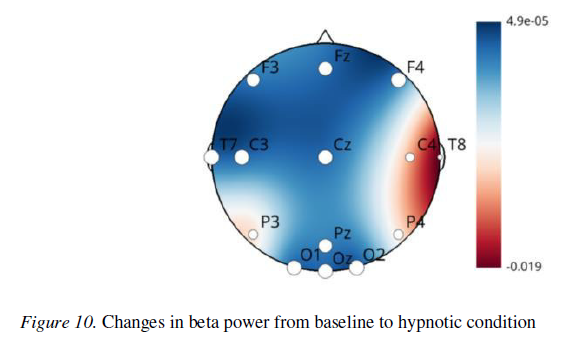
After an extensive literature review and the application of advanced statistical methods, I found that spectral power alone does not serve as a reliable indicator of hypnotic susceptibility. However, distinct patterns of increased functional connectivity between specific brain regions were observed in highly hypnotizable individuals — a result that remained statistically significant even after Bonferroni correction.
These findings suggest that the neural basis of hypnotizability may lie less in localized activity and more in the integration and communication between brain networks.
My tasks were:
- Data extraction using Python
- Learning signal processing from scratch
- Calculation of key figures
- Selection and application of statistical methods
- Formulation and illustration of the results in the form of a master’s thesis
- Formulation and illustration of the results in the form of a scientific article